Sandstone stands as one of nature’s most remarkable gifts to architecture and design. This sedimentary rock, formed over millions of years, combines unparalleled durability with breathtaking natural beauty. From ancient temples that have withstood centuries to modern homes seeking an organic aesthetic, sandstone continues to be a premier choice for builders, architects, and homeowners worldwide.
This comprehensive 10,000-word guide will take you on an in-depth exploration of sandstone, covering:
- Its geological formation and unique properties
- The compelling reasons to choose sandstone for your projects
- Its diverse applications in construction and design
- How to select the finest quality sandstone
- Proper maintenance techniques
- Innovative uses in contemporary architecture
- Why Ubesh Sandstone and Labour Contractor (USSW) stands as your ideal partner
By the end of this guide, you’ll possess expert-level knowledge about sandstone and understand exactly why it should be your material of choice for any building or landscaping project.
Chapter 1: Understanding Sandstone – Nature’s Architectural Masterpiece
What is Sandstone?
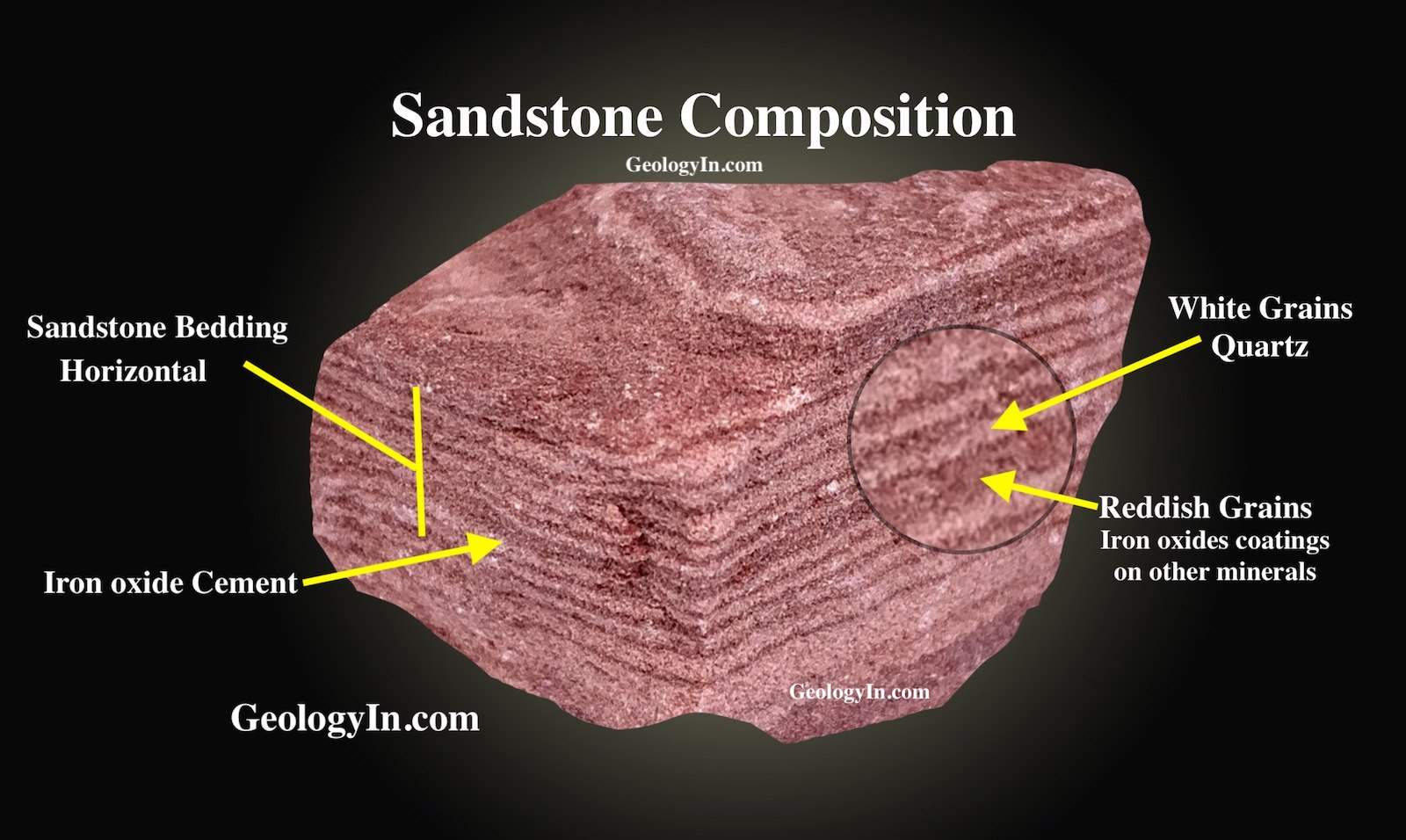
Sandstone represents one of Earth’s most fascinating geological creations. This clastic sedimentary rock consists primarily of:
- Mineral particles (typically 0.0625mm to 2mm in diameter)
- Quartz and feldspar as dominant components
- Natural cementing materials like silica, calcium carbonate, or iron oxide
What makes sandstone truly remarkable is its formation process. Unlike igneous rocks formed from molten magma or metamorphic rocks transformed by heat and pressure, sandstone tells a story of gradual accumulation and natural cementation over extraordinary timescales.
The Geological Journey: Formation of Sandstone
The creation of sandstone is a slow, meticulous process that unfolds across three key stages:
- Erosion and Weathering
- Existing rocks break down through physical and chemical weathering
- Wind, water, and ice gradually reduce parent rocks to sand-sized particles
- This process can take thousands to millions of years
- Transportation and Deposition
- Particles are carried by wind, rivers, or ocean currents
- They eventually settle in layers in environments like:
- River deltas
- Desert dunes
- Beach shores
- Lake beds
- Lithification (Compaction and Cementation)
- Overlying sediment layers create immense pressure
- Mineral-rich water percolates through, depositing cementing agents
- Complete solidification may require 5-50 million years

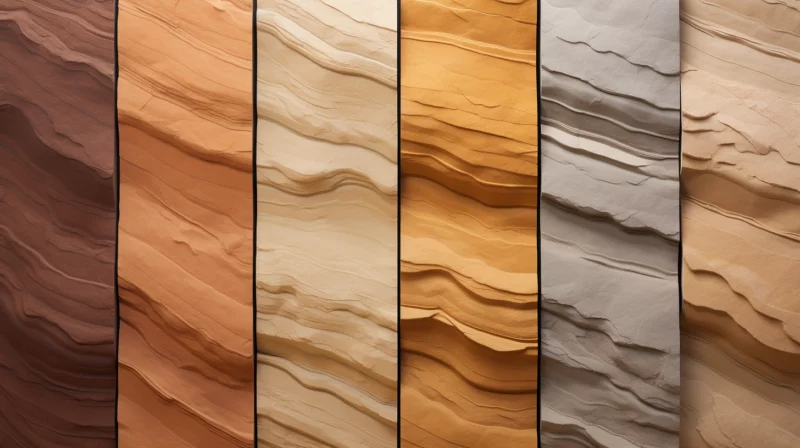
Diverse Types of Sandstone
Sandstone’s characteristics vary significantly based on its mineral composition and formation environment:
| Type | Composition | Key Features | Best Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quartz Sandstone | >90% quartz grains | Extreme durability, light colors | High-traffic flooring, heavy construction |
| Arkose | 25%+ feldspar | Pink/red hues, coarse texture | Decorative walls, monuments |
| Lithic Sandstone | Abundant rock fragments | Dark colors, variable hardness | Paving, rustic construction |
| Greywacke | Clay matrix with angular grains | Dark gray, very hard | Foundations, heavy-duty use |
| Calcareous Sandstone | Contains calcium carbonate | Softer, reacts with acid | Carvings, indoor decor |

Exceptional Properties of Sandstone
Sandstone’s unique characteristics make it ideal for numerous applications:
- Porosity and Permeability
- Natural pore structure allows water drainage
- Ideal for outdoor applications where water runoff is crucial
- Porosity typically ranges from 5% to 25%
- Remarkable Durability
- Compressive strength: 20-170 MPa
- Weather resistance surpasses many synthetic materials
- Withstands freeze-thaw cycles when properly sealed
- Workability
- Mohs hardness typically 6-7 (comparable to granite)
- Can be cut, carved, and shaped with relative ease
- Accepts various finishes from polished to rough-hewn
- Thermal Properties
- Natural insulator with high thermal mass
- Helps regulate indoor temperatures
- Surface remains cool underfoot in hot climates
- Aesthetic Versatility
- Available in warm earth tones to cool grays
- Natural color variations create visual interest
- Takes stains and finishes exceptionally well
Chapter 2: Why Sandstone Outperforms Other Building Materials
1. Unmatched Strength and Longevity
Sandstone’s track record speaks for itself:
- Historical Evidence: Structures like Petra (2000+ years old) demonstrate longevity
- Modern Testing: Compressive strength comparable to concrete (20-170 MPa)
- Weather Resistance: Performs exceptionally in:
- Extreme temperature variations
- Heavy rainfall environments
- Coastal areas with salt exposure
Case Study: The Red Fort in Delhi, built in 1639, showcases sandstone’s endurance against centuries of monsoons, pollution, and temperature extremes.
2. Aesthetic Versatility for Every Design Vision
Sandstone offers unparalleled design flexibility:
Color Spectrum:
- Warm tones: Honey, buff, pink, red
- Cool tones: Gray, blue-gray, greenish hues
- Variegated options with natural color blending
Surface Finishes:
- Polished: Glossy, refined appearance (slip-resistant when textured)
- Honed: Smooth matte finish, ideal for contemporary spaces
- Flamed: Thermal treatment creates anti-slip texture
- Bush-hammered: Rustic, heavily textured surface
- Sandblasted: Uniform matte finish with subtle texture
Design Applications:
- Traditional carved details
- Modern minimalist surfaces
- Rustic natural textures
- Precision-cut geometric patterns

3. Low-Maintenance Luxury
Contrary to some natural stones, sandstone requires minimal upkeep:
Maintenance Routine:
- Daily Care: Simple dust mopping or sweeping
- Weekly Cleaning: pH-neutral stone cleaner with warm water
- Annual Maintenance: Reapplication of penetrating sealer
Stain Prevention:
- Immediate blotting of spills
- Use of coasters under glasses
- Quick cleanup of oil-based substances
Long-Term Preservation:
- Professional deep cleaning every 2-3 years
- Minor chip repairs with color-matched epoxy
- Structural assessment for load-bearing elements

4. Unrivaled Application Versatility
Sandstone’s adaptability makes it perfect for:
Architectural Applications:
- Structural walls and columns
- Flooring (interior and exterior)
- Roofing tiles in traditional architecture
- Staircases and balustrades
Landscape Features:
- Paving stones and stepping stones
- Retaining walls and garden borders
- Water features and fountains
- Outdoor kitchens and fire pits
Decorative Elements:
- Sculptures and art pieces
- Fireplace surrounds
- Feature walls and cladding
- Custom furniture pieces
5. The Sustainable Choice
Sandstone stands out as an eco-friendly building material:
Environmental Benefits:
- Low Embodied Energy: Requires minimal processing compared to manufactured materials
- Natural Abundance: Widely available without depleting rare resources
- Thermal Efficiency: Reduces energy needs for heating/cooling
- Long Lifespan: Minimizes replacement and associated waste
Sustainable Practices:
- Responsible quarrying with land rehabilitation
- Water recycling in processing facilities
- Utilization of all stone fragments (zero-waste approach)
- Local sourcing to reduce transportation emissions



